
Non-provisional patent applications are a critical step in securing intellectual property rights for inventors and businesses alike. With the evolving landscape of intellectual property law and the increasing complexity of technological advancements, patent agents play a pivotal role in guiding inventors through this intricate process.
IP Author, an AI-powered drafting platform, stands out as a revolutionary tool designed to streamline and enhance the efficiency of drafting non-provisional patent applications.
See how patent agents can leverage IP Author to effectively file non-provisional patents, ensuring efficiency in patent drafting and compliance with legal requirements.
Key Elements of a Non-Provisional Patent Application
While provisional patent applications offer a cost-effective way for inventors to establish an early filing date for their invention, they expire after 12 months unless followed by a non-provisional application.
Non-provisional patent applications, on the other hand, are comprehensive filings that initiate the formal patent examination process. It is a detailed document submitted to a patent office, such as the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) or the European Patent Office (EPO), to obtain a utility patent.
Each component of the patent application plays a crucial role in defining the invention’s scope, novelty, and utility, ultimately determining the patent’s strength and enforceability. Here are the key elements: of the non-provisional patent application:
- Title: The application should have a descriptive and concise title that accurately represents the invention.
- Specification: The specification is a detailed description of the invention and includes the background of the invention, a summary, a brief description of the drawings (if applicable), and a step-by-step explanation of how to make and use the invention.
- Claims: The claims are the most important part of a patent application, as they define the scope of protection sought. They describe the specific features and elements of the invention that are considered new and non-obvious.
- Drawings: Drawings, if applicable, should be clear, labeled, and provide a visual representation of the invention from different angles or perspectives.
- Abstract: The abstract is a concise summary of the invention that highlights its technical features and advantages. It should be brief and provide potential patent examiners and interested parties with a quick overview of the invention.
- Sequence listing (if applicable): If the invention involves genetic sequences or other complex biological materials, a sequence listing may be required. This listing includes the specific sequence information in a standardized format.
- Oath or declaration: It’s a formal statement that must be made by each inventor to affirm their belief of being the original inventor.
Before submitting the non-provisional patent application, the patent attorney or agent reviews it thoroughly to ensure that all the necessary legal requirements are met and help identify any potential issues or areas for improvement.
It is important to thoroughly fact-check all the information included in the application. This ensures that the claims and descriptions accurately reflect the invention and that there are no inaccuracies or misleading statements.
Enhanced Application Drafting Efficiency in Three Steps
IP Author, developed by Dolcera, an innovation tools and services company, embodies the next generation of patent drafting solutions. It integrates Dolcera’s extensive patent database and AI technologies to offer a streamlined, efficient approach to drafting non-provisional patent applications. Here’s how patent agents can harness IP Author to their advantage:
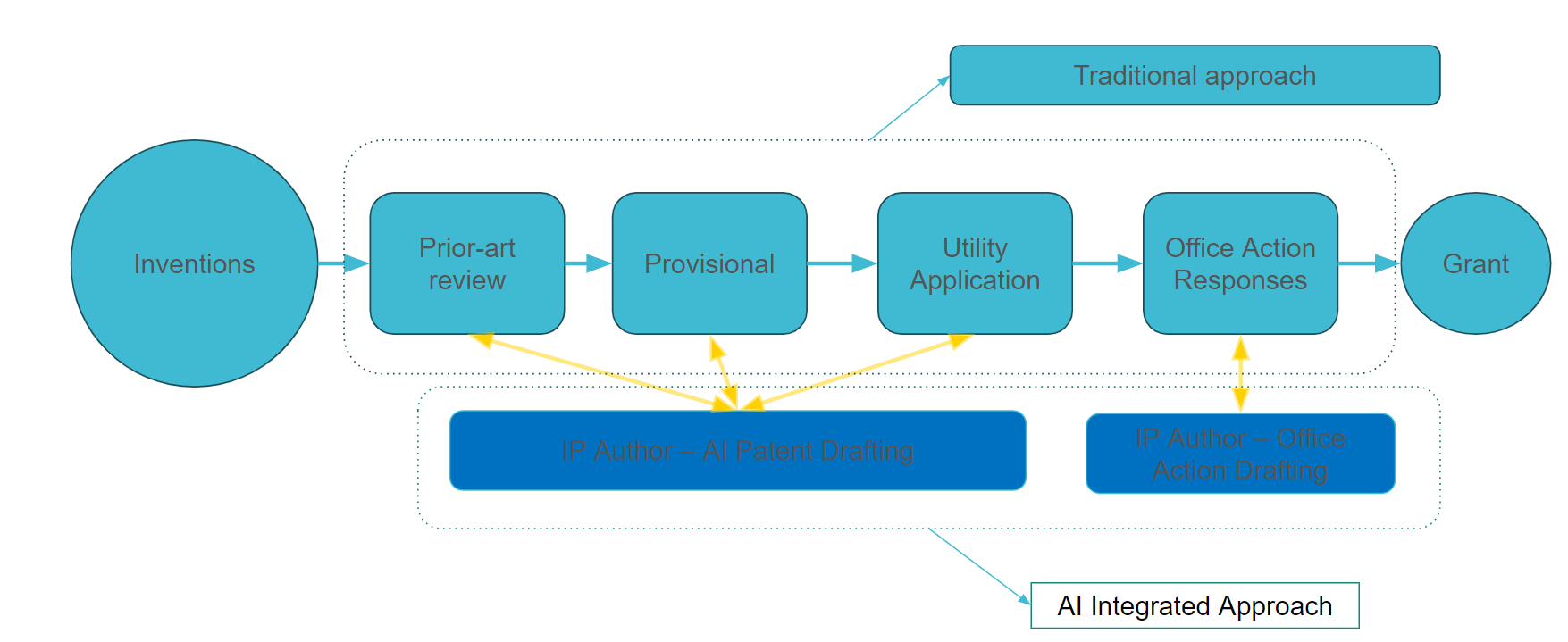
Source – IP Author
1. Describe the Invention
Begin by inputting a comprehensive description of the invention. IP Author’s AI algorithms analyze the input to understand the invention’s nuances. Leverage the tool’s capabilities for efficient draft generation.
2. Prior Art Review
Utilizing Dolcera’s vast database, IP Author conducts an exhaustive search for prior art, ensuring the invention’s novelty and non-obviousness.
Provisional and Utility Patent Application Drafting
The platform generates a complete patent draft, including specifications, claims, and abstract, aligned with legal standards and tailored to the invention’s unique aspects.
Patent agents then analyze the draft provided by IPAuthor, making any necessary adjustments to ensure accuracy and compliance with legal standards.
Why Patent Agents Use AI for Drafting Patent Applications
Patent agents are increasingly turning to automation and artificial intelligence for drafting patent applications to make patent documentation more streamlined, cost-effective, and efficient.
One of the main gains is time savings. IP Author users have reported saving 20-50% of drafting time, allowing agents to focus on strategic aspects of patent prosecution.“I am spending half the time (saving 10+ hours per patent).” says a patent attorney from a boutique high-tech patent and IP law firm specializing in the procurement, licensing, and litigation of patents and trade secrets.
The quality of patent application drafts produced by AI is high, in turn enabling patent agents to process more patents. According to an IP attorney at a Fortune 500 company, “IP Author is delivering at a fourth-year associate level.”
The process is cost-effective, offering savings on drafting and office action responses, which is advantageous to both patent agents and their clients.
IP Author prioritizes security and confidentiality, employing strict data access controls and ensuring that input data is not used for model training or service improvements. This guarantees the protection of sensitive information throughout the drafting process.
Key Considerations for a Successful Non-Provisional Patent Application
Novelty: The invention must be completely new and not disclosed publicly before the filing date. Conducting a thorough prior art search can help identify any similar inventions or existing patents that could affect the novelty of the application.
Non-obviousness: The invention should not be an obvious improvement of existing knowledge or technology. It should involve some level of inventiveness or an unexpected combination of elements.
Enablement: The application should provide enough information for one skilled in the field to understand and reproduce the invention. This includes providing detailed descriptions, clear drawings, and any necessary formulas or calculations.
Utility: The invention should have a practical and useful application. It should offer some kind of advantage, solve a problem, or provide a new and improved solution to an existing issue.
Adequate disclosure: The application should fully disclose the invention and its various aspects. This includes describing the preferred embodiments, alternative designs, and any possible variations or modifications.
Timeliness: It is crucial to file the non-provisional patent application within the appropriate time frame to secure protection. In most countries, this is typically within one year of the first public disclosure or offer for sale of the invention.
Explore AI-Assisted Patent Drafting Options
The drafting of non-provisional patent applications represents a critical juncture in the patent procurement process. Once granted, a non-provisional patent provides exclusive rights to the inventor, preventing others from making, using, selling, or importing the invention without permission.
IP Author offers a cutting-edge solution for patent agents, streamlining the drafting process through its AI-powered platform. By ensuring high-quality, compliant applications, IP Author not only enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of patent agents but also significantly contributes to advancing innovation and protecting intellectual property rights in the digital age.